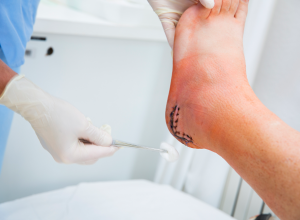
Ankle Fracture
A broken ankle is known in the medical world as an ankle fracture. Fractures of the ankle are one of the most common bone and joint injuries.
Ankle fractures can range in severity from less serious avulsion injuries (like those resulting from a fall or sporting accident) to complicated comminuted fractures (when the bone shatters into multiple fragments, typically caused by trauma like vehicular accidents).
Ankle fractures can affect all of the bones in your ankle, including the tibia (shinbone), fibula and talus, as well as the medial malleolus (inside part of the tibia), posterior malleolus (back part of the tibia) and the lateral malleolus (end of the fibula). Ankle fractures can also affect the ankle, syndesmosis and subtalar joints as well as the ankle ligaments. If both the tibia and fibula bones are broken, it is called a bimalleolar fracture.
Symptoms
Most people who experience an ankle fracture have the following symptoms:
- Pain in the foot, ankle and leg
- Severe swelling of the ankle, foot and leg
- Bruising at the site of the break
- Immobility of the limb (difficulty walking and/or standing)
Ankle fractures and less serious ankle sprains typically have the same symptoms, so it’s important to seek medical attention right away. Failure to visit a podiatrist, orthopeadic surgeon or other doctor could lead to osteomyelitis (infection of the bone), deformity, arthritis, chronic pain and an extended recovery time.
Some people may see the ankle bones protruding from the skin. This is called an open fracture and it requires immediate medical attention. Failure to seek treatment could lead to serious infections.
Causes
Bone fractures are the result of a physical force, high impact stress or trauma being exerted on the bone, causing it to break, crack or shatter. Most people call the condition a broken bone, but doctors use the term bone fracture.
Ankle fractures are typically caused by trips and falls, sporting accidents, twisting or rolling the ankle, and car accidents.
Broken ankles affect people of all ages, but older adults experience the condition more often that others. This is due to bones becoming brittle as we age, as well as increased odds of falling.
Other things can can cause ankle fractures include smoking, which reduces bone density, and underlying diseases that weaken the bone (cancer and osteoporosis, for example). The latter type of fracture is called a pathologic fracture.
Treatment
Most doctors recommend conservative, non-surgical treatment of bone fractures, regardless of the bone affected. Conservative treatment includes pain management with medications like ibuprofen and immobilization in a splint or in a plaster or fiberglass cast.
Surgical treatment methods are typically reserved for very serious ankle fractures and fractures that do not respond to conservative treatment options.
Healing Time
Recovery for ankle fractures differes greatly depending on the age and health of the patient. Bones take at least six weeks to heal, but aging adults may experience several months of recovery time.
No matter the case, it’s very important to follow your doctor’s guidelines for after-fracture care. Failure to do so can lead to arthritis, osteomyelitis (infection of the bone), malunion (when the bone heals in a less than optimal position), chronic pain and even foot deformity.
For more information on bone fractures, check out our Bone Fracture Wiki page.
Notice concerning medical entries:
Articles having medical content shall serve exclusively for the purpose of general information. Such articles are not suitable for any (self-) diagnosis and treatment of individual illnesses and medical indications. In particular, they cannot substitute for the examination, advice, or treatment by a licensed physician or pharmacist. No replies to any individual questions shall be effected through the articles.






