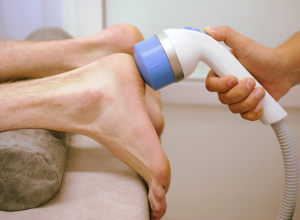
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT)
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (sometimes referred to as ESWT) is a noninvasive treatment method that sends shockwaves to the body’s tissue. It is usually used to treat tendonopathies like Achilles tendonitis, plantar fasciitis, and calcific tendinitis when anti-inflammatory and immobilization devices don’t work. Each shockwave administered with the therapy is said to create microtrauma, which stimulates new blood flow to the afflicted area and assists in healing.
The US FDA has approved ESWT for the treatment of only plantar fasciitis and epicondylitis (tennis elbow). However, it is used to treat other tendinopathies like Achilles tendinopathy in the UK, as the National Institute for Health and Excellence states there are no major safety concerns associated with ESWT.
A typical extracorporeal shockwave therapy session for the treatment of the plantar fascia usually lasts about 10 minutes. It is unclear, however, if ESWT is truly effective.
Notice concerning medical entries:
Articles having medical content shall serve exclusively for the purpose of general information. Such articles are not suitable for any (self-) diagnosis and treatment of individual illnesses and medical indications. In particular, they cannot substitute for the examination, advice, or treatment by a licensed physician or pharmacist. No replies to any individual questions shall be effected through the articles.






